The truss is to be designed using seasoned f22 grade jarrah timber.
Finding roof loading on a truss at joints chegg.
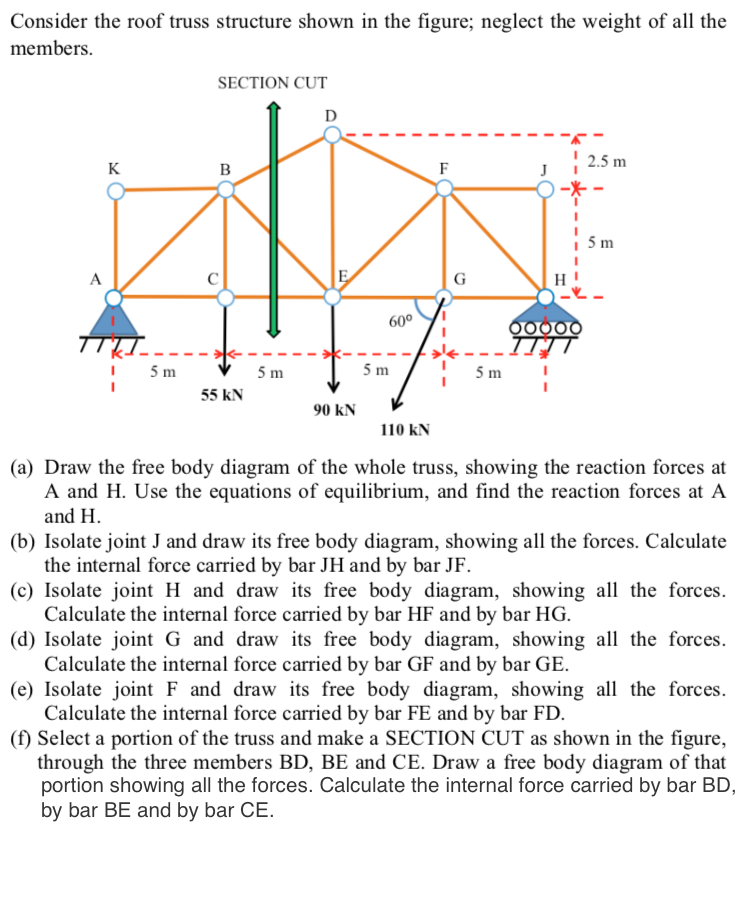
The truss in fig.
3 determine the loads on the roof truss based on the tributary area and the load path.
The roof truss shown is one of a series of trusses spaced 16 ft center to center.
4 determine the external reactions.
State whether each member is in tension or compression.
Cm 1 0 ct 1 0 and ci 1 0.
For f1 8 6 and p 17 2.
Truss joints are assumed to be pin connected.
The reaction at eis p f1 f1 f1 f1 b в 2 m 2 m h 2 m g 2 m f 2 m select one.
The roofing panels span between purlins see loads and load paths lab notes which carry the roof loads to the truss joints.
Fasteners do not reduce the area off the members.
Self weight of the timber can be ignored in the analysis and design of the truss.
Use the method of joints for both numbers to determine the force in each member of the roof truss shown.
Trusses are spaced 24 in o c and the roof live load is to be in accordance with the ibc.
0459 a snow load transfers the forces shown to the upper joints of a pratt roof truss.
Neglect any horizontal reactions at the supports and assume all members are in tension.
The roof is simply supported on purlins which in turn are attached to the joints at the top chord of the truss.
25 8 o b 5 7 o c.
39 2 the internal force in member ef.
7 b supports a roof dead load of 16psf.